Follow us on Facebook
Breaking updates in your feed — tap to open
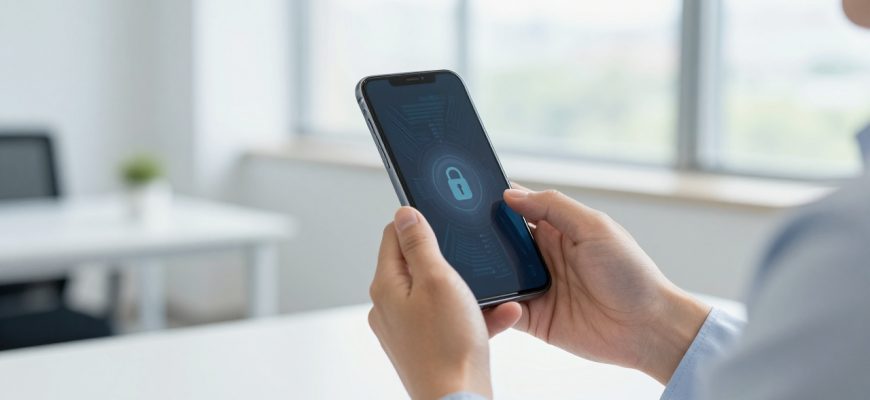
The mobile security landscape is changing profoundly in our approach to 2026, with sophisticated protection systems that require advanced threats compelling businesses to offer sophisticated protection against them. Formerly an enterprise technology is increasingly being made accessible to consumers and professionals tasked with sensitive data on personal machines. This is a paradigm shift in our attitude towards the security of smartphones and tablets, and the boundaries between the protection of corporate and personal devices are blurred.
- Hardware-Isolated Work Profiles Overview
- Sophisticated Mobile Device Management (MDM) Systems
- Secured Industrial Communication Solutions
- Comparison of iOS and Android Security Implementations
- Professionals Must Organize a Clear Separation
- Pragmatic Data Protection Advice
- Camera and Mobile Photography Security Issues
- The Future of Mobile Security
Hardware-Isolated Work Profiles Overview
One of the most important developments in mobile security architecture is hardware-isolated work profiles. These systems build physically isolated environments on a single device so that corporate data and personal applications and information are completely isolated. On Android, this is usually provided via Knox Workspace or other secure containers, and on iOS the more integrated method of Managed Apple IDs and application-specific protection is used. Implementation varies widely across platforms, yet the fundamental idea is the same, which is to establish an impassable boundary between professional and personal digital realms.
Sophisticated Mobile Device Management (MDM) Systems
Sophisticated mobile device management (MDM) systems have grown past rudimentary remote wiping systems by providing fine-tuning operational control and access to data. Contemporary MDM systems are able to implement encryption policies, block application installation on the basis of security certificates, and follow suspicious activity in real-time. To those in the field that use personal devices to do their job, these can offer the necessary level of oversight without interfering too much with the personal privacy provided they are properly set up. The trick is in solution-balanced implementation, which preserves user autonomy without compromising organization security.
Secured Industrial Communication Solutions
Secured industrial communication solutions have become key to individuals dealing with vital data. In addition to regular messaging apps, such specialized tools also include end-to-end encryption, self-destruction message capabilities, and the ability to send files securely. Their particular advantage lies in the fact that they are compatible with existing enterprise authentication systems and only authorized personnel can gain access to confidential communications. Such protection is now more relevant due to the tightening of regulatory requirements on data privacy and transmission security.
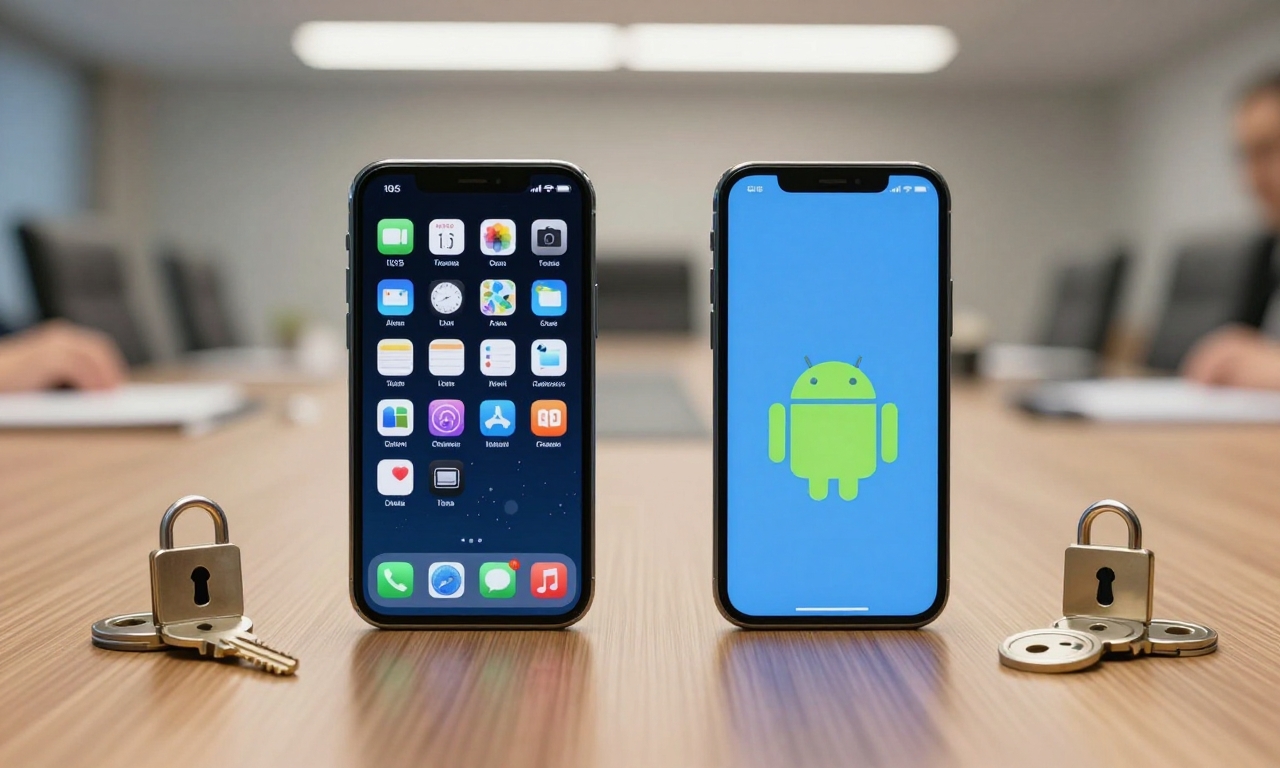
Comparison of iOS and Android Security Implementations
IOS and Android have entirely different design philosophies as they approach security differently. The walled-garden approach used by Apple offers the same level of security to all devices, with encryption at the hardware level and regular and mandatory updates. Android open system is more flexible but needs more cautious setting up to reach the same level of protection. Android releases in the recent past have improved security in many ways such as Google Play Protect and increased permissions control that have helped bridge the differences between the two platforms.
When deciding between platforms, professionals are often left with specific use cases and organizational needs, and in this case, iOS tends to be more securely configured out of the box with less configuration than other platforms. It is the best selection among organizations with a small IT team. Android offers businesses greater flexibility in terms of the security aspects required, but it involves more technical skill to do it right. The two platforms are also now capable of hardware security modules and biometric authentication, which protects against unauthorized access rather effectively.
Professionals Must Organize a Clear Separation
Professionals must organize a clear separation between work and personal work when working with sensitive data on personal devices. This starts by locking work related applications and data to separate profiles or containers. Personal device security is based on regular security testing of applications installed, close attention to permissions, and software updates. Furthermore, by making sure that there are effective authentication procedures that go beyond mere passwords (biometric authentication or security keys) there is further protection layers.

Pragmatic Data Protection Advice
Performance and battery life optimization is of special concern when operating security applications, which sometimes can be resource-heavy. Numerous security functionalities such as background checks and continuous encryption may affect battery life and performance of the device. The professionals are advised to balance on the need to ensure security and the need to be usable, maybe running intensive security checks during the charging weekend or even changing the settings according to the prevailing threat conditions. New gadgets that have powerful processors and big batteries can cope with these tasks like never before.
Camera and Mobile Photography Security Issues
The feature of camera and mobile photography introduces distinct security issues, since high-resolution pictures usually include metadata that can result in the disclosure of privacy or sensitive places. Workers must turn off geotagging on work-related pictures and apply secure listing and transferring apps on visual information. Excellent camera systems in flagship smartphones though useful in documentation, have to be handled with caution to avoid unwanted data leakage in embedded information in image files.
The Future of Mobile Security
The future of mobile security is probably going to entail a further integration of hardware whereby security processors will be a matter of course in every device. With the growing popularity of foldable phones and the development of 5G networks, new attack vectors will arise, demanding dynamically implemented security measures. Our professions must be aware of new threats and be applied to apply existing best practices that provide a security stance that balances protection and the realistic usability in our now-more-mobile-dependent working areas.








