Follow us on Facebook
Breaking updates in your feed — tap to open
As digital regulation evolves globally, age verification requirements are becoming increasingly common across apps and websites. From social platforms to gaming services, developers face growing legal mandates to confirm users’ ages, particularly for content or features restricted to adults. Currently, this responsibility falls primarily on individual app developers, creating both privacy concerns and user experience challenges. However, a compelling case exists for Apple to implement centralized age verification across its ecosystem-leveraging the company’s established privacy infrastructure to create a more secure, efficient solution.
This approach would address two critical problems simultaneously: protecting user privacy by minimizing sensitive data exposure and streamlining the verification process for both users and developers. With Apple’s existing trust model demonstrated through features like Apple Pay and passkeys, the company possesses the technical capability to verify identity without compromising personal information. As legislation like the proposed App Store Accountability Act considers shifting responsibility to platform providers, examining Apple’s potential role becomes increasingly relevant for the future of digital privacy and compliance.
- The Growing Age Verification Landscape
- Privacy Concerns with Current Verification Methods
- Document-Based Verification
- Biometric Verification
- Apple’s Privacy-First Infrastructure
- Apple Pay and Privacy
- Passkeys and Authentication
- Safari Privacy Features
- How Centralized Age Verification Could Work
- Single Verification Process
- App and Website Integration
- Safari Browser Implementation
- Benefits for Users and Developers
- User Experience Improvements
- Developer Advantages
- Implementation Challenges and Considerations
- Technical Implementation
- Regulatory Compliance
- Privacy and Security
- Market Adoption
- The Future of Digital Age Verification
- Regulatory Trends
- Privacy Expectations
- Technical Capabilities
The Growing Age Verification Landscape
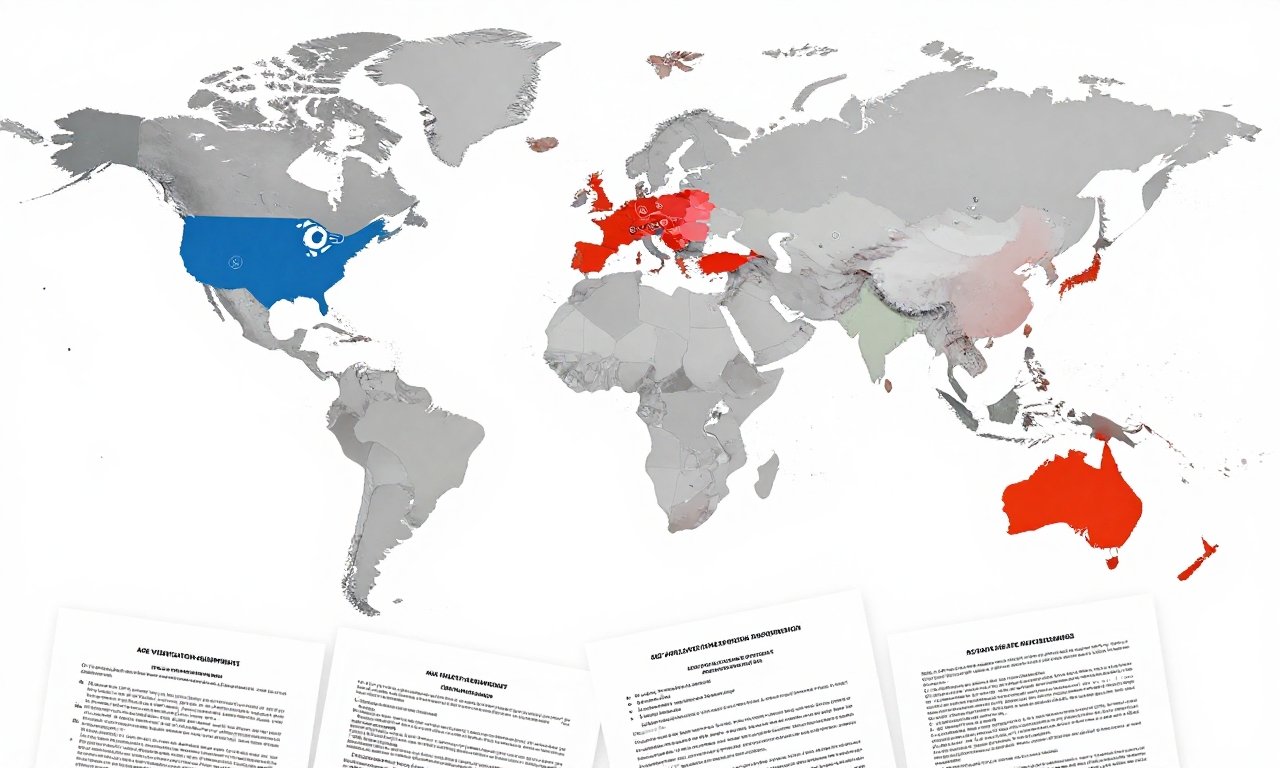
Age verification requirements are expanding rapidly across multiple jurisdictions, creating a complex compliance landscape for app developers and website operators. In the United States, several states have implemented or proposed laws mandating age verification for certain types of content, particularly social media platforms and adult-oriented services. Internationally, countries like Australia have established similar requirements, with the European Union considering broader digital age verification frameworks as part of its digital services regulations.
Currently, each developer or service provider must implement their own verification system when operating in regulated markets. This decentralized approach creates several challenges:
- Inconsistent user experience: Users encounter different verification methods across various apps and websites
- Privacy risks: Multiple services collecting and storing sensitive identification documents
- Compliance complexity: Developers must navigate varying requirements across different jurisdictions
- Implementation costs: Smaller developers face significant expenses to build and maintain verification systems
The proposed App Store Accountability Act represents a potential shift in this landscape, suggesting that platform providers like Apple could bear responsibility for age verification. This legislative direction acknowledges the practical challenges of decentralized verification while recognizing platform providers’ technical capabilities to implement more robust solutions.

Privacy Concerns with Current Verification Methods
Most current age verification systems require users to submit sensitive personal information, creating significant privacy vulnerabilities. Common verification methods include:
Document-Based Verification
Users typically submit government-issued identification documents, such as driver’s licenses or passports, to prove their age. This approach presents multiple privacy concerns:
- Data exposure: Each service receives and stores complete identification documents
- Security risks: Multiple databases containing sensitive information increase breach vulnerability
- Identity theft potential: Complete identification documents in multiple locations create identity theft opportunities
Biometric Verification
Some services use facial recognition or video selfies to estimate age or verify identity against documents. While potentially more convenient, these methods raise additional concerns:
- Biometric data collection: Facial recognition data represents particularly sensitive personal information
- Accuracy concerns: Age estimation algorithms can produce false results, particularly across different demographics
- Consent complexity: Users may not fully understand how their biometric data will be used or stored
The cumulative effect of these verification methods across multiple apps creates what privacy advocates describe as a “verification nightmare”-users repeatedly submitting their most sensitive personal information to numerous services, each with varying security standards and data protection practices.
Apple’s Privacy-First Infrastructure
Apple has developed a sophisticated privacy infrastructure that could support centralized age verification while maintaining user privacy. Several existing Apple features demonstrate the company’s approach to identity verification without data exposure:
Apple Pay and Privacy
Apple Pay represents a successful model for secure transactions without sharing payment details with merchants. The system uses device-specific numbers and unique transaction codes, ensuring that actual card numbers remain private. This approach demonstrates how Apple can facilitate verification (of payment capability) without exposing sensitive information to third parties.
Passkeys and Authentication
Apple’s implementation of passkeys provides passwordless authentication using public-key cryptography. This system allows users to sign into websites and apps without creating passwords that could be breached or phished. The technical approach-keeping private keys on the user’s device-could be adapted for age verification while maintaining similar privacy protections.
Safari Privacy Features
Apple’s web browser includes multiple privacy protections, including Intelligent Tracking Prevention and Privacy Report. These features demonstrate Apple’s commitment to limiting data collection during web browsing-a principle that could extend to age verification through Safari without compromising user privacy.
These existing systems provide technical foundations that could support age verification while aligning with Apple’s stated privacy principles, particularly the concepts of data minimization and on-device processing.
How Centralized Age Verification Could Work
A centralized Apple age verification system would function similarly to existing privacy-preserving verification methods. The proposed approach would involve several key components:
Single Verification Process
Users would verify their age once through a secure Apple process, potentially using:
- Face ID or Touch ID biometric authentication
- Government ID verification through secure Apple servers
- Age confirmation through trusted third-party services
Once verified, Apple would generate a privacy-preserving token confirming the user meets age requirements without revealing specific age or identity details.
App and Website Integration
Developers would integrate with Apple’s verification system through APIs, similar to Sign in with Apple. When an app or website requires age verification:
- The service requests age verification through Apple’s system
- Apple presents a verification request to the user
- Upon approval, Apple provides a verification token to the service
- The service receives confirmation that the user meets age requirements without accessing personal data
Safari Browser Implementation
For websites requiring age verification, Safari could implement a similar system:
- Websites could request age verification through browser APIs
- Safari would handle the verification process without exposing user data to the website
- Verified status could be maintained for specified periods or sessions
This approach would significantly reduce the privacy risks associated with current verification methods while improving user experience through single verification.

Benefits for Users and Developers
Centralized age verification through Apple would provide substantial advantages for all stakeholders in the digital ecosystem:
| Stakeholder | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Users | Reduced privacy risks, simplified verification process, consistent experience across services, fewer data submissions |
| App Developers | Reduced compliance complexity, lower implementation costs, standardized approach, access to trusted verification |
| Website Operators | Simplified age-gating implementation, reduced liability, improved user experience, privacy compliance |
| Regulators | More consistent compliance, verifiable systems, reduced fraud potential, privacy protections |
User Experience Improvements
From a user perspective, centralized verification would transform a currently frustrating process. Instead of repeatedly submitting identification documents or undergoing facial recognition for each age-restricted service, users would verify once through a trusted provider. This approach aligns with modern expectations for seamless digital experiences while actually enhancing privacy protections.
Developer Advantages
For developers, particularly smaller operations, centralized verification would reduce both technical and compliance burdens. Rather than building and maintaining complex verification systems-and ensuring they meet evolving regulatory requirements-developers could integrate with Apple’s established system. This would allow them to focus resources on core app functionality rather than compliance infrastructure.
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of centralized age verification are substantial, several implementation challenges would need addressing:
Technical Implementation
Building a secure, scalable verification system requires significant technical resources. Apple would need to:
- Develop robust verification methods that work globally
- Ensure system reliability and availability
- Maintain strong security against potential attacks
- Provide developer tools and documentation for integration
Regulatory Compliance
Different jurisdictions have varying requirements for age verification, including:
- Specific verification methods required
- Data retention requirements
- Audit and reporting obligations
- Age thresholds for different types of content
Apple’s system would need to accommodate these variations while maintaining consistent privacy protections.
Privacy and Security
Even with Apple’s privacy focus, centralized verification creates a single point of potential vulnerability. The system would require:
- Strong encryption and security measures
- Transparent privacy policies
- Independent security audits
- Clear data minimization practices
Market Adoption
Successful implementation would require broad adoption by both developers and users. Apple would need to:
- Make integration straightforward for developers
- Ensure user trust in the verification process
- Potentially mandate use for App Store submissions in regulated categories
Despite these challenges, Apple’s existing infrastructure and privacy reputation position the company well to address them effectively.
The Future of Digital Age Verification
As age verification requirements continue to expand globally, centralized solutions like Apple’s proposed system represent a promising direction for balancing regulatory compliance with user privacy. Several factors suggest this approach will become increasingly important:
Regulatory Trends
Legislators are increasingly recognizing the limitations of decentralized verification systems. Proposed legislation like the App Store Accountability Act indicates growing interest in platform-level solutions that can provide more consistent, verifiable compliance.
Privacy Expectations
Users are becoming more aware of privacy risks associated with repeated data submission. Systems that minimize data exposure while providing necessary verification align with evolving consumer expectations and privacy regulations like GDPR.
Technical Capabilities
Advances in privacy-preserving technologies, including zero-knowledge proofs and secure multi-party computation, could enable even more sophisticated verification systems that provide necessary confirmation without any data exchange.
“The fundamental challenge of digital age verification isn’t technical-it’s about creating systems that respect user privacy while meeting legitimate regulatory requirements. Apple’s infrastructure suggests a path forward that could achieve both objectives.”
While some privacy advocates argue against age verification entirely, the reality is that such requirements are becoming increasingly common across digital services. In this context, centralized verification through trusted providers like Apple represents a preferable alternative to the current fragmented approach-offering better privacy protections, improved user experience, and more consistent compliance.
As Apple continues to position itself as a privacy-focused company, implementing a centralized age verification system would demonstrate practical commitment to this principle while addressing a growing need in the digital ecosystem. For users, developers, and regulators alike, such a system could transform age verification from a privacy concern into a privacy-protecting feature of the digital landscape.